Demodex infestation requires immediate, aggressive treatment by doctor, patient
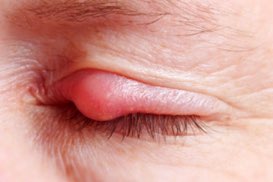
We have all seen the chronic blepharitis patient that has attempted numerous unsuccessful treatment regimens and has visited numerous eye doctors looking for some relief. Interestingly, the cause of their chronic blepharitis might be secondary to Demodex infestation.
Pathogenic role of Demodex mites in blepharitis
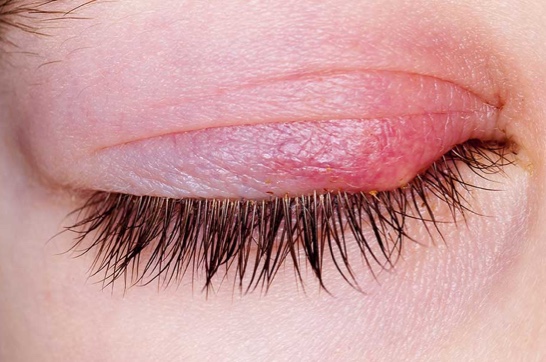
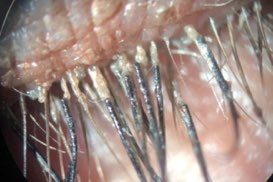
Two distinct Demodex species have been confirmed as a cause of blepharitis: Demodex folliculorum can cause anterior blepharitis associated with disorders of eyelashes, and D. brevis can cause posterior blepharitis with meibomian gland dysfunction and keratoconjunctivitis. Tea tree oil treatments with either 50% lid scrubs or 5% lid massages are effective in eradicating mites and reducing ocular surface inflammation.
Eye Mites Symptoms and Causes
Many people complain of red, irritated, scratchy and sometimes swollen or thickened eyelids. The diagnosis is often a condition called blepharitis. Eye doctors have ways to treat blepharitis that are usually successful. However, sometimes the condition does not respond to treatment because the doctor is focusing on treating the wrong contributing organism. Sometimes the underlying problem is eye mites.
Demodex blepharitis: clinical perspectives
Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis are two mites which infest the human eye and which may, in excess, lead to a wide range of anterior segment findings. Demodex mites have been implicated in anterior and posterior blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, blepharokeratitis, and beyond. Due to significant overlap with other anterior segment conditions, Demodex infestation remains underdiagnosed and undertreated. Definitive diagnosis can be made with lash sampling, and the most common mode of treatment is with tea tree oil in varying concentrations. This article summarizes elements of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management critical to clinical care of this common condition.